ANSI/HL7 V3 INFOB, R1-2010 HL7 Version 3 Standard: Context-Aware Retrieval Application (Infobutton); Knowledge Request, Release 1 7/21/2010 |
 HL7 V3 IG INFOBUTTON, R2 INFORM 2008JUN HL7 Version 3 Implementation Guide: URL-Based Implementations of the Context-Aware Retrieval Application (Infobutton) Domain, Release 2 June 2008 |
 HL7 V3 IG INFOBUTTON, R3 INFORM 2010DEC HL7 Version 3 Implementation Guide: URL-Based Implementations of the Context-Aware Retrieval Application (Infobutton)Domain, Release 3 December 2010 |
 HL7 V3 IG SOA KM INFOBUTTON, DSTU R1 2011MAR HL7 Version 3 Implementation Guide: URL-Based Implementations of the Context-Aware Retrieval Application (Infobutton)Domain, Release 3 March 2011 |
Content Last Edited: 2012-08-14T11:54:42
2.2 Storyboards
2.3 Application Roles
2.4 Trigger Events
2.5 Refined Message Information Models
2.6 Hierarchical Message Descriptions
2.7 Interactions
2.A Implementation Guide for Context-aware Knowledge Retrieval (Infobutton)
Clinicians face numerous knowledge needs during the course of patient care. To a large extent, these knowledge needs are related to gaps in medical knowledge that clinicians need to fill in order to make, confirm, or carry out a patient care decision. Ultimately, knowledge gaps lead to suboptimal decisions, compromising the quality of care.
With the advent of the World Wide Web, numerous online health knowledge resources have become available. Although these resources have demonstrated great potential to resolve clinicians' and their patients' knowledge needs, a number of barriers hinder a more efficient and effective use of these resources, slowing their dissemination. In essence, both patients and providers become overwhelmed with the vast amount of information available, raising the need for tools that help them identify relevant, context-specific, high quality knowledge in a timely manner.
To lower barriers to the access of knowledge resources at the point of need, researchers have proposed context-aware integration of knowledge resources into clinical information systems (CIS), such as electronic health record (EHR) and personal health record (PHR) systems. Tools that provide this type of integration have been generically denominated infobuttons. The goal of the present specification is to facilitate the context-aware integration of knowledge resources into CISs.
In a typical infobutton implementation, a CIS places hyperlinks adjacent to clinical concepts, such as medications, laboratory tests, and problems. These hyperlinks embed a knowledge request with a set of attributes that capture the context of the interaction between the user and the CIS. Context can be expressed in terms of attributes that characterize (1) the clinical concept of interest (e.g., a medication, a laboratory test result, a problem list entry); (2) the patient (e.g., demographics); (3) the CIS task (e.g., order entry, laboratory results review, problem list review); (4) the knowledge user (e.g., discipline, specialty, language, patient vs. provider); and (5) the care setting (e.g., outpatient, inpatient). When a user clicks on an infobutton, the following steps are followed: 1) a request for knowledge is sent to a decision support system known as infobutton manager; 2) Using these context attributes, the infobutton manager produces a refined knowledge request, for example, asking for specific content topics that are thought to be most relevant in the particular context (e.g., diagnosis, treatment). The refined knowledge request is submitted to one or more relevant knowledge resources; 3) the knowledge resources responds with knowledge content that fulfills the knowledge request; 4) the infobutton manager processes the content from the multiple resources and sends it to the CIS.
Figure 1 depicts a typical implementation approach to knowledge integration using the Context-Aware Knowledge Integration standard specification. As indicated in the diagram, the present Knowledge Request specification enables a CIS (e.g., EHR, PHR) to request context-specific knowledge from knowledge resources. A specification for the response of knowledge resources will be addressed in a separate future specification.
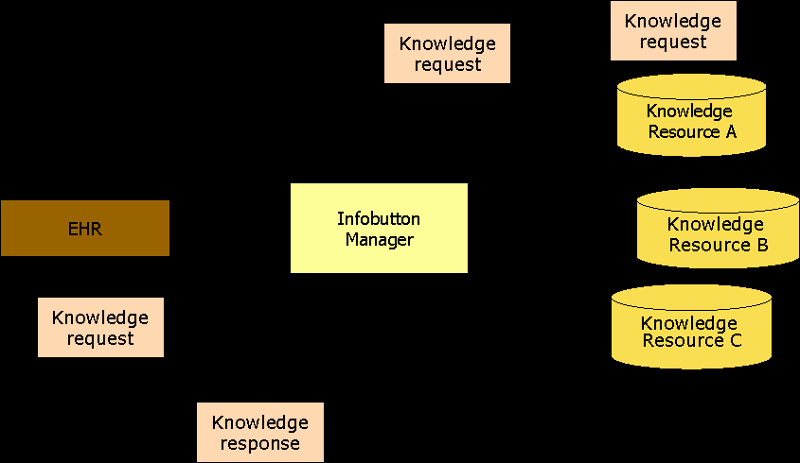
Infobutton managers are one of many possible implementation mechanisms for context-aware knowledge integration. In other alternative implementations, infobuttons submit requests for knowledge directly to a knowledge resource without the mediation of an infobutton manager. In addition, knowledge can be integrated into a CIS through mechanisms other than infobutton hyperlinks. This standard specification is agnostic of any particular implementation and is designed to support a variety of context-aware knowledge integration approaches.
The following notes should be considered when reading this specification:
- Although both the knowledge request and knowledge response interactions are described in this specification, the specification only includes the knowledge request information model. An information model for the knowledge response will be part of a separate specification.
- The specification does not determine how the components involved in a knowledge integration scenario should be implemented.
- The specification does not specify a standard indexing and content structure for knowledge resources. However, knowledge resource developers can use this standard as a guideline to define their indexing and content structure, enabling their product to more effectively respond to a CIS that submits knowledge requests based on this specification.
To be compliant with this standard, implementers are not required to handle all the data elements defined in the knowledge request RMIM. In order to promote rapid adoption, the following directives should be followed:
- A CIS SHOULD formulate knowledge requests as complete as possible, using as many context data elements as possible, preferably using coded data.
- Except for required classes and attributes, knowledge resources MAY process only the elements that they can handle, ignoring other elements. For example, if a knowledge resource does not use patient.administrativeGender as a content index, the resource MAY ignore this attribute whenever it is included in a knowledge request.
These directives allow a CIS to create knowledge requests that can be fulfilled by knowledge resources with varying levels of sophistication. The approach also enables less sophisticated knowledge resources to quickly achieve compliance without major modifications to their content and indexing structure. Still, resources MAY be gradually enhanced aiming at fully exercising the message model described in this specification.
|
||||||
|
For details on the interpretation of this section, see the storyboard discussion in the Version 3 Guide.
The following storyboard depicts a typical context-aware knowledge retrieval transaction. Although the present specification focuses primarily on the Knowledge Request step, the storyboard also includes the knowledge response step in which a knowledge resource fulfills a knowledge request. As previously mentioned, the latter step will be covered in a separate future specification.
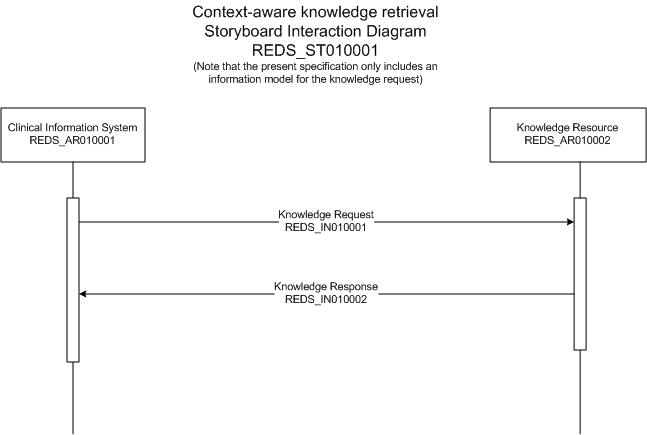
| Infobutton Knowledge Request |
Table 1 - Storyboard: Knowledge request originated from a problem list.
| Step | Specification | Actor | Description |
| 1 | Knowledge request | EHR | A clinician is reviewing a problem list module of an EHR and is unfamiliar with a rare disease (Camurati-Engelmann Disease) that the patient, a 15-year-old female, has. The problem list module provides an infobutton link next to the "Camurati-Engelmann Disease" problem. The user clicks on the infobutton link. |
| 2 | Knowledge request | EHR | Context data available to the EHR captured and submitted in a knowledge request to the knowledge resource. |
| 3 | Knowledge response | Knowledge resource | The knowledge resource receives the request and looks for content in its content collection that is deemed to be relevant based on the elements included in the knowledge request. |
| 4 | Knowledge response | Knowledge resource | The knowledge resource submits a knowledge response with content that may be relevant in this particular context. |
|
||||||||
|
For details on the interpretation of this section, see the discussion of application roles and their relationships in the Version 3 Guide.
|
||||||
|
For details on the interpretation of this section, see the discussion of trigger events in the Version 3 Guide.
| Type: | User request |
| State Transition: | InfobuttonEventNotification (REDS_RM010001UV) |
Context-aware knowledge request event initiated by the CIS (e.g., as a result of a user clicking on an Infobutton).
|
||||||
|
For details on the interpretation of this section, see the description of RMIMs in the Version 3 Guide.
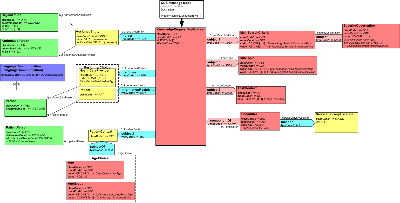
| Parent: | Structured Document (REDS_DM000001UV) |
KnowledgeRequestNotification class
This class represents the root of the KnowledgeRequestNotification RMIM. The following are definitions of the attributes of the KnowledgeRequestNotification class:
- KnowledgeRequestNotification.id: Represents the globally unique instance identifier of a knowledge request.
- KnowledgeRequestNotification.effectiveTime: creation time of the knowledge request.
KnowledgeRequestNotification Relationships
This section describes classes related to the root KnowledgeRequestNotification class:
MainSearchCriteria: represents the main subject of interest in a knowledge request (e.g., a medication, a lab test result, a disease in the patient's problem list). When multiple instances of this class are present, knowledge resources MAY determine whether to join the multiple instances using the AND vs. OR Boolean operator.The following are attributes of the mainSearchCriteria class:
- MainSearchCriteria.code: indicates that the type of this Observation class is KnowledgeSubjectObservationType.
- MainSearchCriteria.value: the primary knowledge subject of interest (e.g., a medication, a laboratory test, a condition).
CD data type restrictions for mainSearchCriteria.value: 1) displayName SHALL be always present, so that knowledge resources that do not support a given code system MAY still process the request using displayName as a search keyword; 2) If code is present, codeSystem SHALL be also present; 3) originalText represents the human readable representation of the code as displayed to the user in the CIS and SHOULD be used only if different than the displayName.
SeverityObservation: specifies the interpretation of a laboratory test result (e.g., 'high', 'low', 'abnormal', 'normal'). This class MAY be used to support implementations where the MainSearchCriteria consists of a laboratory test result. Supports questions such as "what are the causes of high serum potassium?"
- SeverityObservation.code: a code that defines that the type of the observation is SeverityObservation.
- ObservationInterpretation.code: a code that represents the value of the observation interpretation (e.g., high, low, normal)..
SubTopic: narrows down the knowledge request by specifying a subdomain of interest r(e.g., indications, contra-indications, dose) related to the MainSearchCriteria knowledge subject. In Infobutton implementations, the SubTopic may be selected by the user from an Infobutton page that presents a list of content areas that are relevant in a specific context (e.g., "contra-indications of digoxin", "adverse effects of digoxin").
- SubTopic.code: defines that the type of this Observation class is KnowledgeSubtopicObservationType
- SubTopic.value: a code that represents a knowledge subtopic of interest (e.g., diagnosis, treatment, adverse effects).
TaskContext: the task that the user is performing in the CIS when a knowledge request is initiated (e.g., order entry, laboratory results review, problem list review, medications list review).
- TaskContext.code: a code that represents the task that is being performed in an CIS system.
Encounter: the type of patient encounter (e.g., inpatient, outpatient) in which the knowledge request takes place..
- Encounter.code: a code that represents the type of encounter (e.g., inpatient, outpatient).
DeliveryLocation: clinical facility where the patient care is taking place at the time the knowledge request is initiated. MAY be used by the request filler to identify potential local knowledge resources (e.g., local protocols) that are specific to the facility where the patient care is being delivered.
- DeliveryLocation.id: identifier of the facility where the patient care takes place.
KnowledgeRequestNotification Participants
This section describes participants of the KnowledgeRequestNotification RMIM.
AssignedEntity: entity (e.g., institution) that initiated the request. MAY be used by a knowledge request recipient to determine the knowledge resources that the requesting entity has access to (e.g., based on subscriptions). In addition, allows the identification of an individual within the institution, so that personal preferences can be considered by a knowledge request filler when processing the request.
- AssignedEntity.name: username used by the entity (typically as part of an institutional subscription to a knowledge resource)
- AssignedEntity.certificateText: password associated with the username of the entity
Organization: the entity within which the request is initiated.
- Organization.id: identifier of the organization within which the request was initiated
- AuthorizedPerson: the individual who initiated the knowledge request
- AuthorizedPerson.id: username of the person who initiated the request. MAY be used by a knowledge request filler to apply personal preferences during the user's session.
PatientContext: information about the patient that MAY be used by the CIS in a knowledge request to further specify the context in which a knowledge need arises.
- PatientPerson.administrativeGenderCode: gender of the patient represented in the knowledge request.
PerformerChoice: defines the type of Participants that act as the Performer (user who interacts with the system) and InformationRecipient (person who will consume the content). The performer and informationRecipient can be instantiated as a Patient or HealthCareProvider class. Three scenarios are possible: 1) when a care provider interacts with the system seeking knowledge to fulfill his/her own needs, both the performer and informationRecipient SHALL be a HealthCareProvider; 2) when a care provider initiates the knowledge request, but looking for educational information to be given to the patient, the ierformer SHALL be a HealthCareProvider and the informationRecipient SHALL be associated with a Patient; and 3) when a patient is looking for information to fulfill her own needs, both the performer and the informationRecipient SHALL be a Patient.
Age: age of the patient as a numeric value.
- Age.code: a code that indicates that the type of this observation is AgeObservationType..
- Age.value: the patient's age as a numeric quantity. Units SHOULD be expressed in one of the following units (per the Unified Code for Units of Measure): years (a), months (mo), weeks (wk), days (d), or hours (h).
AgeGroup: an observation that represents the patient's age in terms of a predefined coded age range (e.g., infant, neonate).
- AgeGroup.code: a code that indicates that the type of this observation is AgeGroupObservationType.
- AgeGroup.value: a code that represents the patient's age group.
PerformerChoice Relationships
LanguageCommunication: language of the performer or informationRecipient. In implementations, language of the performer MAY be used by to determine the language of the individual who initiated a knowledge request, while language of the informationRecipient MAY be used to determine the language of the individual who will consume the content. For example, when a clinician looks for patient education information, the clinician's language may be English, while the patient is a Spanish speaker. In this case, while the user interface for the clinician can be presented in English, the requested patient education content will be presented in Spanish.
- LanguageCommunication.code: A code that represents the person's language (e.g., English, Spanish).
| CDS Message Model | REDS_HD010001UV01 |
|
||||||
|
For details on the interpretation of this section, see the description of HMDs in the Version 3 Guide.
|
||||||||
|
For details on the interpretation of this section, see the definition of Interactions in the Version 3 Guide.
Infobutton knowledge request initiated by the CIS (typically as a result of a user clicking on an Infobutton). The knowledge request is submitted to the knowledge resource.
| Trigger Event | Knowledge Request | REDS_TE010001UV01 |
| Transmission Wrapper | Send Message Payload | MCCI_MT000100UV01 |
| Control Act Wrapper | Trigger Event Control Act | MCAI_MT700201UV01 |
| Message Type | Event Notification | REDS_MT010001UV01 |
| Sender | Clinical Information System | REDS_AR010001UV01 |
| Receiver | Knowledge Resource | REDS_AR010002UV01 |
Knowledge resource response to an infobutton knowledge request. As previously mentioned, note that the message payload for this interaction is outside the scope of this specification.
| Trigger Event | Knowledge Request | REDS_TE010001UV01 |
| Reason | Trigger Event | Interaction |
| REDS_TE010001UV01 | REDS_IN010002UV01 |
| Sender | Knowledge Resource | REDS_AR010002UV01 |
| Receiver | Clinical Information System | REDS_AR010001UV01 |
This Annex holds three Implementation Guides that have been developed for use with the Infobutton standard.
URL-Based Implementations of the Context-Aware Information Retrieval (Infobutton) Domain, Release 2
URL-Based Implementations of the Context-Aware Information Retrieval (Infobutton) Domain, Release 3
| Return to top of page |